
Fig. 1. This shows a positive correlation between long-term variations in upper mesospheric ozone (red) and solar ultraviolet (blue).
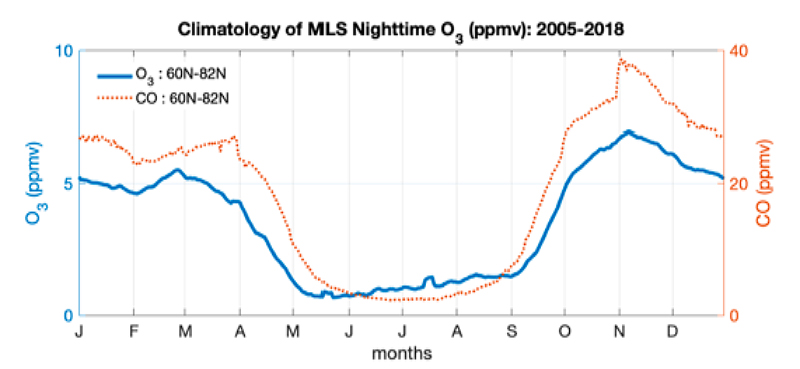
Fig. 2. Climatology (for 2005-2018) of MLS nighttime O3 (blue) and CO (red) at 0.002 hPa (near 90 km) for latitudes 60°N–82°N.
Technical description of figure:
Figure 1. Shown in red are high latitude (a) Northern Hemisphere (60°N–82°N) and (b) Southern Hemisphere (60°S–82°S) zonal mean MLS ozone anomalies (ppmv) during early winter (November/December for the North and March/April for the South) at 0.002 hPa. The overlaid blue curves are SORCE SOLSTICE UV values (in W/m2/nm) at 240 nm to illustrate the UV variation during the same period. The error bars are standard deviations based on daily values during the two months of analysis.
Figure 2. Blue: Climatology of MLS nighttime ozone volume mixing ratio (ppmv) at 0.002 hPa during the MLS observation period (2005–2018) for northern hemisphere high latitudes (60°N–82°N). Red: the same, but for MLS nighttime CO abundances.
Scientific significance, societal relevance, and relationships to future missions:
This work is significant for our improved understanding of the variations in upper atmospheric ozone, which protects the Earth from the harmful effects of solar UV radiation. In terms of future satellite data, there are very few confirmed plans for future missions such as MLS with a focus on global vertically-resolved composition measurements from the upper troposphere to the upper mesosphere.
Data Sources:
Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) data are publicly available from https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets?keywords=MLS&page=1. SORCE SOLSTICE UV data are publicly available from https://lasp.colorado.edu/home/sorce/data/ssi-data/solstice-high-resolution-daily-product/.
References: Lee, J. N., and Wu, D. L. (2020), Solar cycle modulation of nighttime ozone near the mesopause as observed by MLS, Earth and Space Science, 6, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EA001063.
7.2020