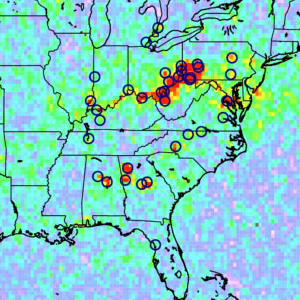
Sulfur dioxide (SO2), emitted from both man-made and volcanic activities, significantly impact air quality and climate. Advanced sensors including the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) have been employed to measure SO2 pollution.
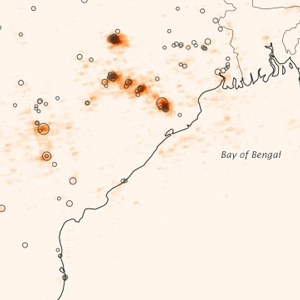
The analysis of data captured by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) found that emissions of sulfur dioxide from Indian power plants have increased by more than 60 percent between 2005 and 2012
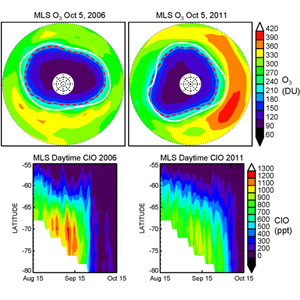
MLS ClO in the 2011 Antarctic vortex was 20% lower than 2006, yet the 2011 ozone hole is very similar to the 2006 hole, the largest ever observed.
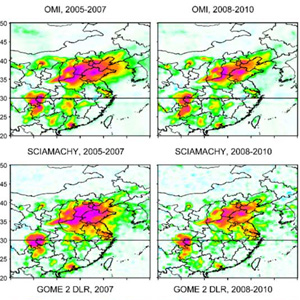
Satellite mapping of sulfur dioxide (SO2) is useful to track volcanic and anthropogenic emissions in places where detailed SO2 emission information is not available.
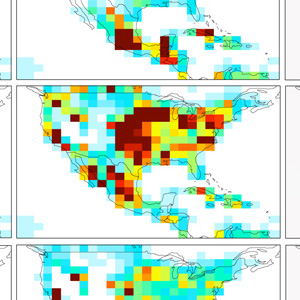
Ammonia (NH3) pungently affects air quality. It is also involved in the formation of aerosol PM2.5 particles, which have adverse health effects, and impacts soil acidification, biodiversity, and the nitrogen cycle.
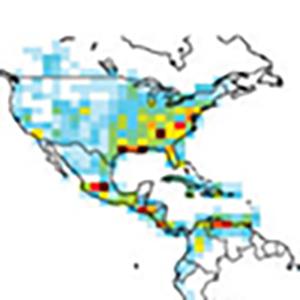
(Science Daily article)
A new NASA-led study uses TES data to find that when it comes to combating global warming caused by emissions of ozone-forming chemicals, location matters.