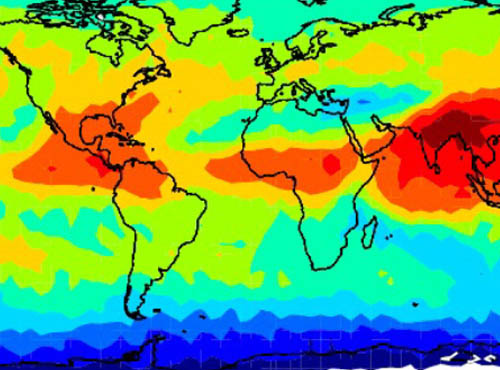
 The SPARC Water Vapor Assessment II
The SPARC Water Vapor Assessment IIAn assessment of satellite humidity measurements was undertaken by the SPARC project (Stratosphere-troposphere Processes and their role in Climate), which quantified the accuracy of H2O measured by spaceborne sensors including Aura's Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS).
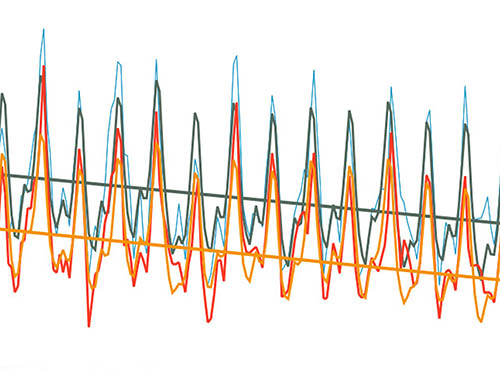 Upper stratospheric ClO and HOCl trends (2005–2020): Aura Microwave Limb Sounder and model results
Upper stratospheric ClO and HOCl trends (2005–2020): Aura Microwave Limb Sounder and model resultsThis work examines trends in upper stratospheric chlorine species for 2005–2020, with an emphasis on chlorine monoxide (ClO) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl), measured by the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) on the Aura satellite.
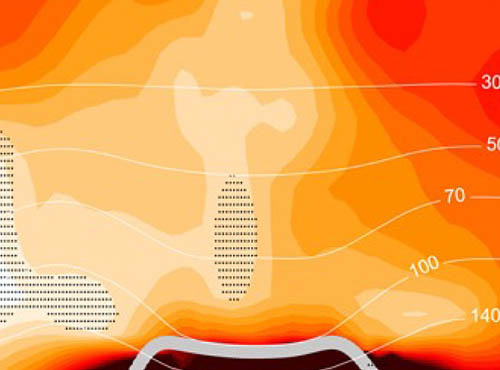
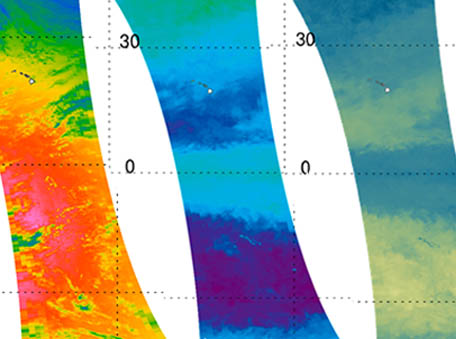
 Hunga Tonga – Hunga Ha’apai Hydration of the Stratosphere
Hunga Tonga – Hunga Ha’apai Hydration of the StratosphereMeasurements of the eruption of the Hunga Tonga – Hunga Ha’apai (HT-HH) underwater volcano from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) revealed that the eruption injected water vapor, SO2, and HCl into the stratosphere.
 Stratospheric Moistening After 2000
Stratospheric Moistening After 2000Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) measurements show substantial and persistent stratospheric moistening following a sharp drop in stratospheric water vapor.
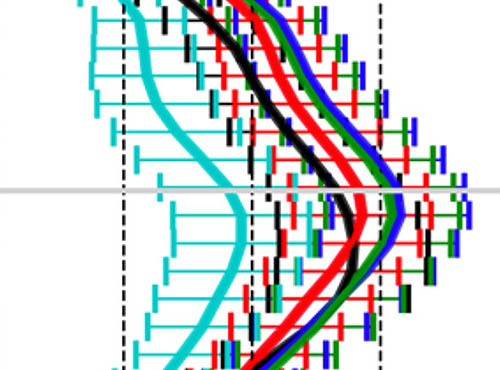 Aura MLS and model simulations reveal a single-peak structure in the solar cycle signal in stratospheric ozone
Aura MLS and model simulations reveal a single-peak structure in the solar cycle signal in stratospheric ozoneOzone profiles measured by the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) over 16 years (2005–2020) were analyzed together with simulations from a 3D chemical transport model using different solar fluxes.
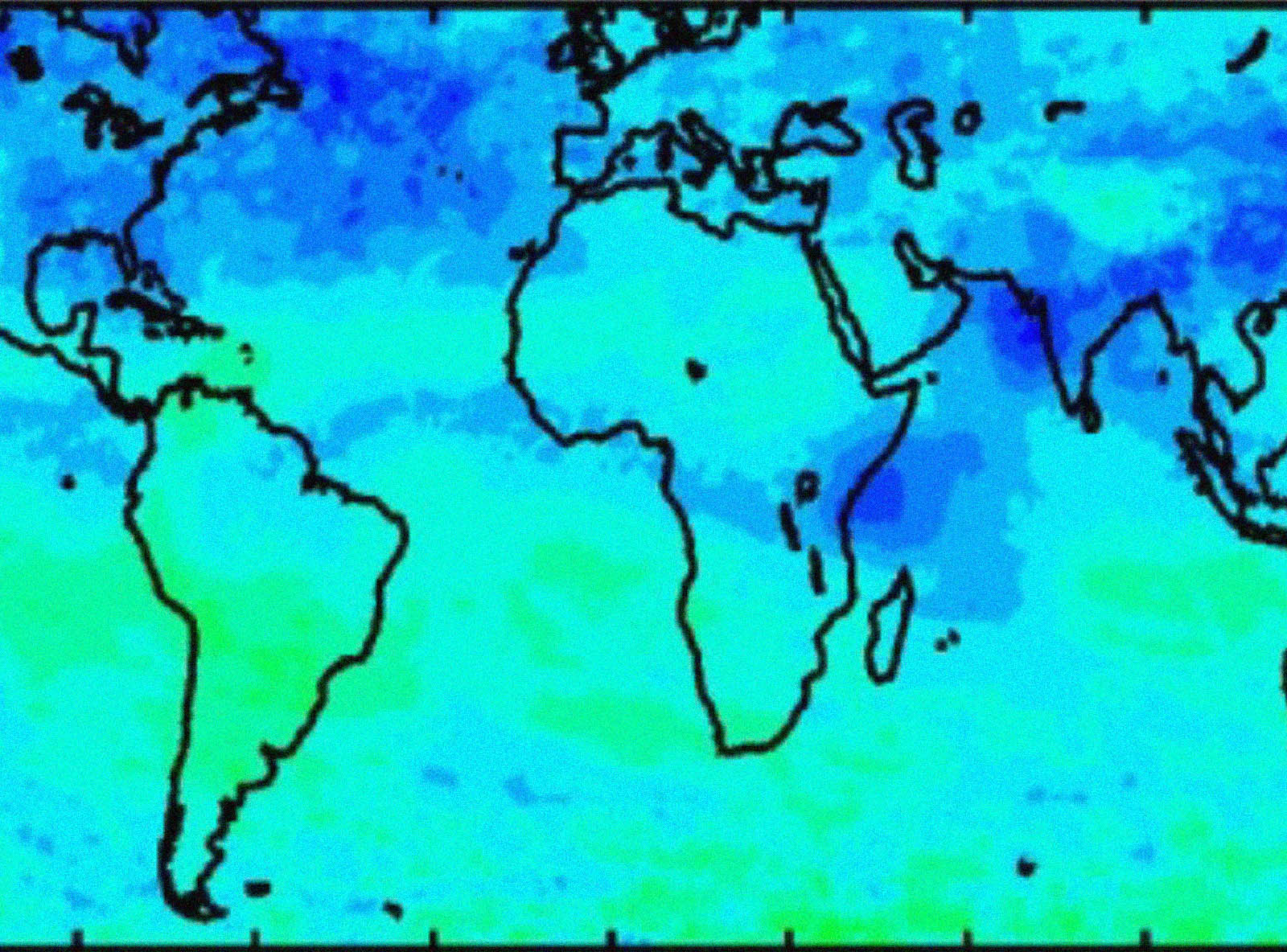 NASA satellite measurements show global-scale reductions in tropospheric ozone in 2020 and again in 2021 during COVID-19
NASA satellite measurements show global-scale reductions in tropospheric ozone in 2020 and again in 2021 during COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic created global scale reductions in anthropogenic sources of pollution including important tropospheric ozone precursors such as nitrogen oxides and Volatile Organic Compounds.
 UV-VIS Spectral Aerosol Absorption
UV-VIS Spectral Aerosol AbsorptionThis Dataset from AERONET-OMI-MODIS Synergy measuring spectral aerosol absorption remains a challenging task in aerosol studies, especially in the UV region, where ground and airborne measurements are sparse.
 Hyperspectral Underwater UV Irradiances
Hyperspectral Underwater UV IrradiancesThe combination of Aqua MODIS and Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) data with a radiative transfer model estimate the penetration depths of solar UV radiation into global ocean.
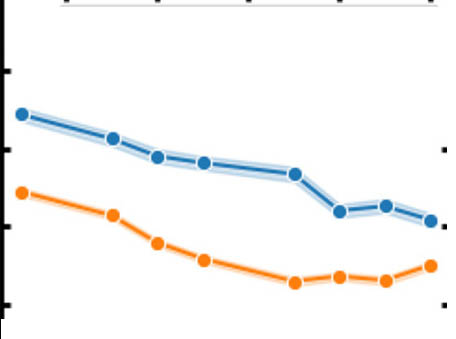 Spatial and Temporal Variation of near Surface Hydroxyl Radical in North American Cities
Spatial and Temporal Variation of near Surface Hydroxyl Radical in North American CitiesCombining Machine Learning and Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) Data to fully measure the hydroxyl radical (OH) which is is the primary cleansing agent in the atmosphere. The abundance of OH in cities initiates the removal of local pollutants; therefore, it serves as the key species describing the urban chemical environment.
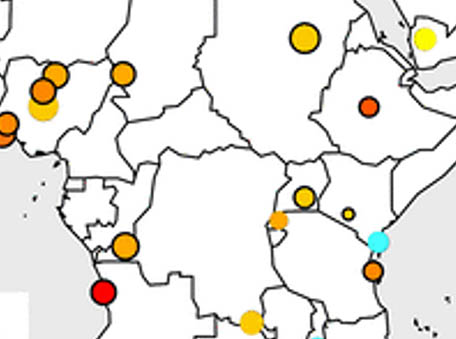 Rapid rise in premature mortality due to anthropogenic air pollution in fast-growing tropical cities from 2005 to 2018
Rapid rise in premature mortality due to anthropogenic air pollution in fast-growing tropical cities from 2005 to 2018Tropical cities are experiencing rapid growth but lack routine air pollution monitoring to develop prescient air quality policies.
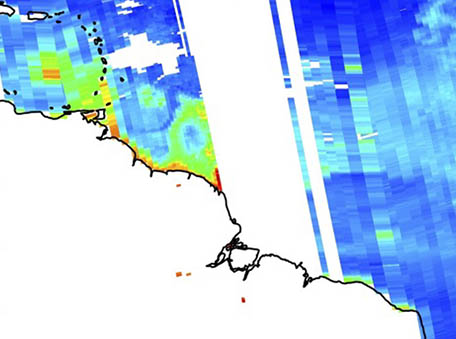 Using Machine Learning for Timely Estimates of Ocean Color Information from Hyperspectral Satellite Measurements in the Presence of Clouds, Aerosols, and Sunglint
Using Machine Learning for Timely Estimates of Ocean Color Information from Hyperspectral Satellite Measurements in the Presence of Clouds, Aerosols, and SunglintWe have developed a new technique to estimate ocean color properties under less-than-ideal retrieval conditions including clouds, aerosols, and sunglint.
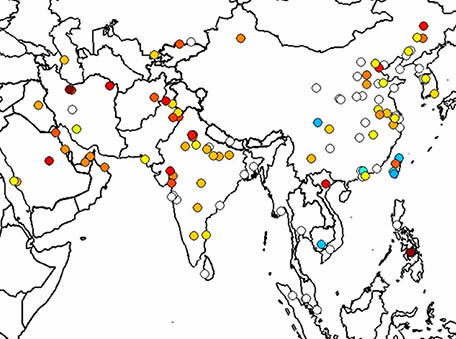 Aura OMI formaldehyde data show significant anthropogenic VOC trends in Asian cities over 2005–2019
Aura OMI formaldehyde data show significant anthropogenic VOC trends in Asian cities over 2005–2019Trends of formaldehyde linked to anthropogenic activity over large cities located in the Asian continent were calculated for the period 2005–2019 using the Quality Assurance for Essential Climate Variables dataset from the Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI).
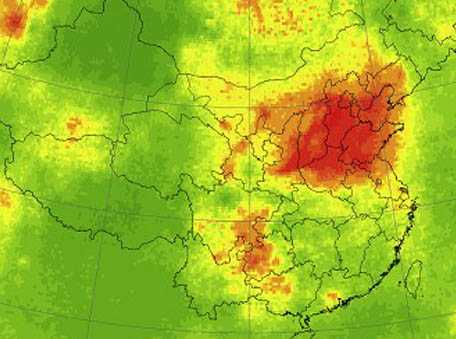 Long-term ambient sulfur dioxide concentration and its exposure risk across China inferred from Aura OMI observations from 2005 to 2018
Long-term ambient sulfur dioxide concentration and its exposure risk across China inferred from Aura OMI observations from 2005 to 2018Although the Sulfur dioxide exposure risk in 2018 decreased significantly from 2005 on a national scale, 80% and 17% of people still faced a high exposure risk in the North China Plain and Northwest China, respectively
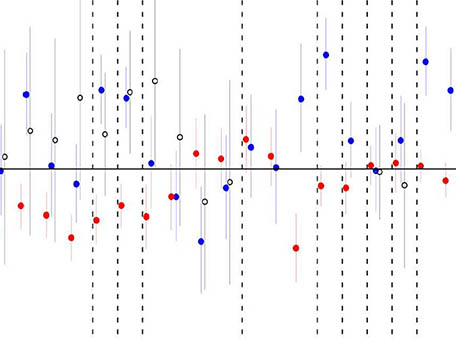 Analysis of recent lower-stratospheric ozone trends in chemistry climate models
Analysis of recent lower-stratospheric ozone trends in chemistry climate modelsAnalyses of monthly zonal mean merged satellite ozone observations that include Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) data as a major component have shown that lower stratospheric ozone over the 50ᵒS-50ᵒN region has been decreasing over the last two decades.
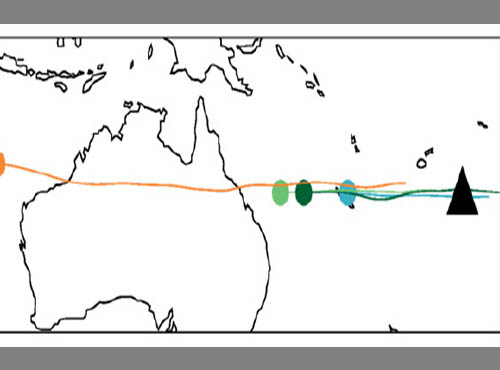
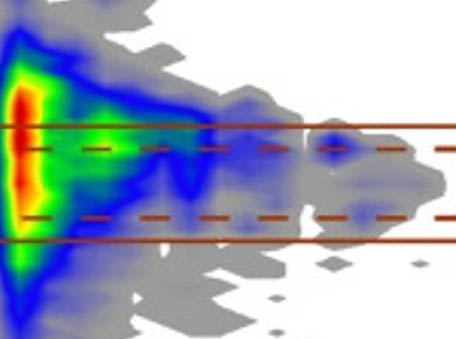
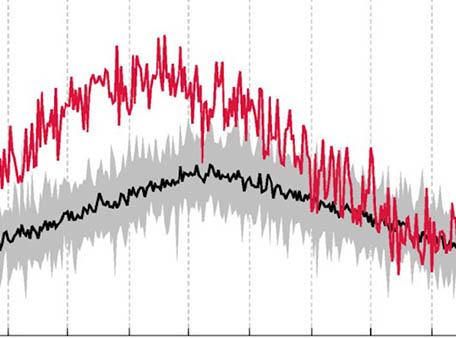 Stratospheric Impacts of the Australian New Year’s Fires
Stratospheric Impacts of the Australian New Year’s FiresThe 2019/2020 Australian New Year’s wildfires (ANY) injected reco.