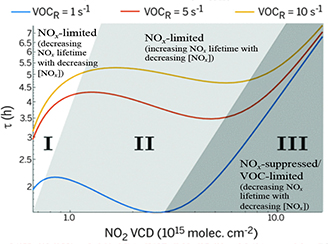
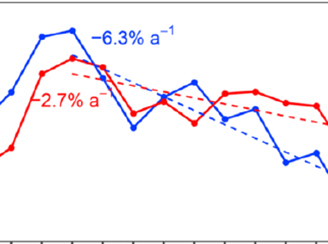
 A shifting lifetime for nitrogen oxides
A shifting lifetime for nitrogen oxides Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument Direct Observation of Changing Nitrogen oxide Lifetime in North American Cities
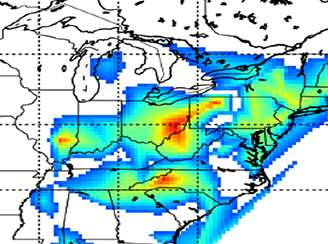
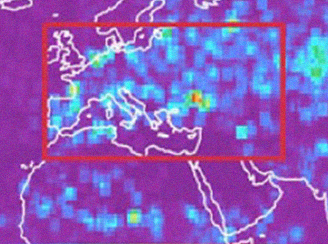 Mid-latitude lightning nitrogen oxides production efficiency
Mid-latitude lightning nitrogen oxides production efficiency Inferred from Ozone Monitoring Instrument and World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN) data
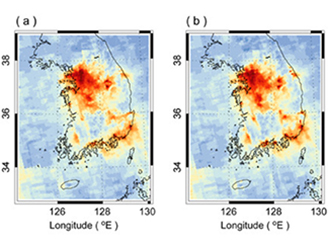 Spatial Downscaling of Nitrogen Dioxide Data
Spatial Downscaling of Nitrogen Dioxide Data Over the last few years, a number of researchers have applied various techniques (e.g., land-use regression models) to create finer-scale Aura OMI NO2 data for use in research. Two recent studies are highlighted here.
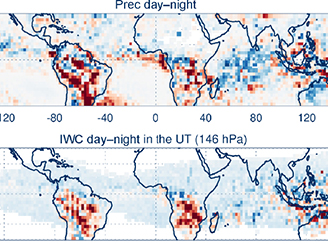 Ice injected into the tropopause by deep convection
Ice injected into the tropopause by deep convection Convective processes play a major role in controlling the abundances of cloud ice and water vapor in the tropical tropopause layer, which in turn strongly modulate climate.
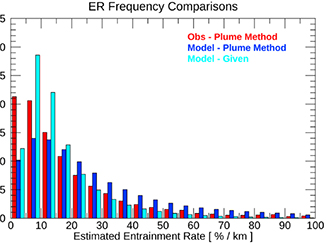 Convective entrainment rates estimated from Aura CO and CloudSat/CALIPSO observations
Convective entrainment rates estimated from Aura CO and CloudSat/CALIPSO observations Entrainment rate (λ) in convective parameterizations is one of the most sensitive, yet uncertain, parameters affecting climate sensitivity, clouds, precipitation, and trace gas distributions.
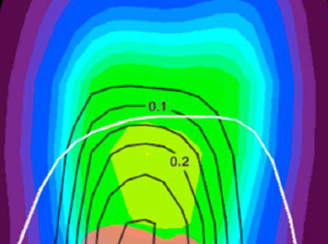 Water vapor, clouds, and saturation in the Tropical Tropopause Layer
Water vapor, clouds, and saturation in the Tropical Tropopause Layer A recent study shows that the high humidity is due to both horizontal transport of air into colder regions, and slow ascent due to radiative heating, both of which lead to cloud formation.
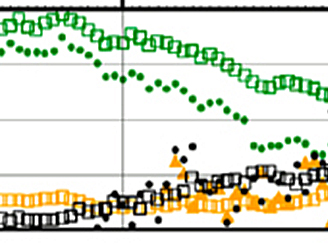 Unusual chlorine partitioning in the Arctic winter lowermost stratosphere
Unusual chlorine partitioning in the Arctic winter lowermost stratosphereLow temperatures in the 2015/16 winter lower stratosphere give rise to polar stratospheric cloud (PSC) formation, denitrification/dehydration, chlorine activation, and chemical ozone loss.
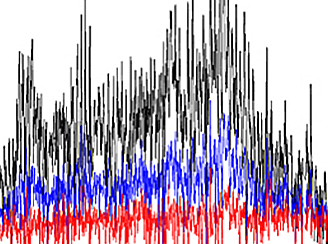 Solar Spectral Irradiances: Comparisons with Independent Datasets and Model Predictions
Solar Spectral Irradiances: Comparisons with Independent Datasets and Model Predictions Climate studies rely on detailed knowledge of the total energy balance, in particular, on the spectral and temporal changes of solar flux. The Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument is uniquely positioned to deliver the required long-term, stable, accurate ~daily solar data that span the entire solar cycle 24.
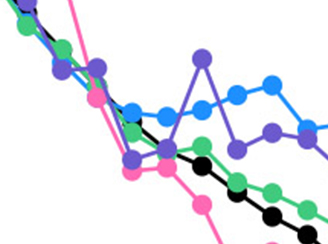 The importance of accounting for the free tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide background
The importance of accounting for the free tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide background Using satellite observations of tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide columns to infer long-term trends in US nitrogen oxide emissions.
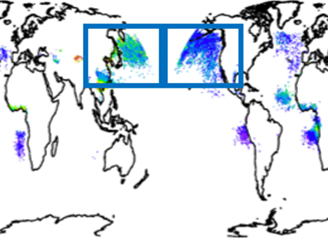 A 12-year long global record of optical depth of absorbing aerosols above the clouds
A 12-year long global record of optical depth of absorbing aerosols above the clouds Quantifying the natural sources variability in the troposphere and lower stratosphere is important for assessing and evaluating anthropogenic impacts on ozone, a trace gas that is important for climate, air quality, and atmospheric chemistry.
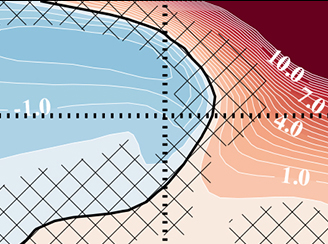 Assessing El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Quasi-biennial Oscillation impacts on ozone variability
Assessing El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Quasi-biennial Oscillation impacts on ozone variability The conventional satellite-based remote sensing aerosol products provide distribution of aerosols in cloud-free regions leaving vast cloudy areas unmonitored in terms of the presence of aerosols.
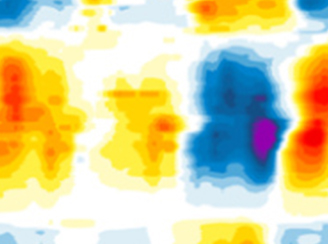 Structural changes in the shallow and transition branch of the Brewer–Dobson circulation induced by El Niño
Structural changes in the shallow and transition branch of the Brewer–Dobson circulation induced by El NiñoThe global meridional overturning of mass in the stratosphere, generally known as the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC), plays a crucial role in Earth’s climate system by controlling the distributions of atmospheric constituents.
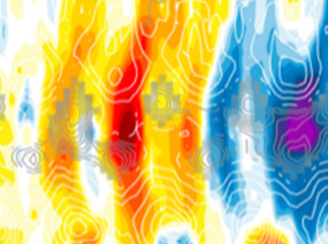 Response of stratospheric water vapor and ozone to the unusual timing of El Niño and the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation disruption of 2015-2016
Response of stratospheric water vapor and ozone to the unusual timing of El Niño and the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation disruption of 2015-2016 Two major modes of climate variability that affect the stratospheric circulation, and consequently trace gas distributions, are the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO).
 On the role of heterogeneous chemistry in ozone depletion and recovery
On the role of heterogeneous chemistry in ozone depletion and recoveryConclusive verification that stratospheric ozone destruction is lessening as expected in response to international controls on anthropogenic ozone-depleting substances (ODSs) enacted under the Montreal Protocol is one of today’s atmospheric science imperatives, but robust detection of such ozone “recovery” is complicated by large natural variability.
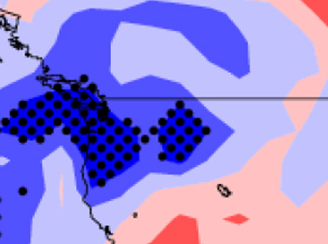 Effects of Arctic stratospheric ozone changes on precipitation in the northwestern United States
Effects of Arctic stratospheric ozone changes on precipitation in the northwestern United States Changes in stratospheric ozone can induce, via atmospheric radiation balance, stratospheric circulation anomalies.
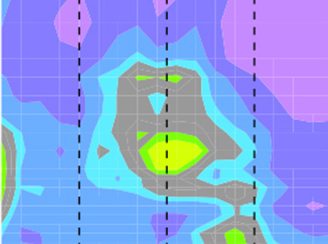 Evaluating models of stratospheric composition
Evaluating models of stratospheric composition How well do a free-running and “nudged” chemistry climate model reproduce global timeseries of upper atmospheric composition (biases, variability, trends)?
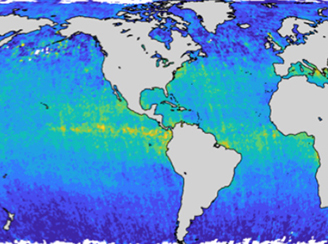 Mapping the Oxidizing Capacity of the Global Remote Troposphere
Mapping the Oxidizing Capacity of the Global Remote Troposphere This new product represents a novel application of existing satellite data and will help us better interpret contemporary trends in the budgets of methane (a potent greenhouse gas) and ozone (a major pollutant and oxidant source).
 OMI Tracks Changes in Mexico’s Offshore Gas Flaring Activity
OMI Tracks Changes in Mexico’s Offshore Gas Flaring ActivityGas flaring from Mexico’s offshore oil fields leads to economic loss and emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases, and there are global efforts to reduce gas flaring.
 OMI Links Decrease in Acid Deposition to Emission Reduction in the Eastern U.S.
OMI Links Decrease in Acid Deposition to Emission Reduction in the Eastern U.S.Introducing a new method using OMI observations to attribute decrease in acid deposition to SO2 emission reduction
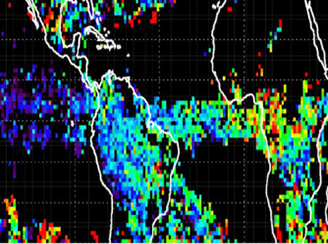 The Nature of Ozone in Deep Convective Clouds As Measured from Aura OMI/MLS
The Nature of Ozone in Deep Convective Clouds As Measured from Aura OMI/MLSOMI satellite measurements reveal for the first time many key features of ozone variability inside deep convective clouds
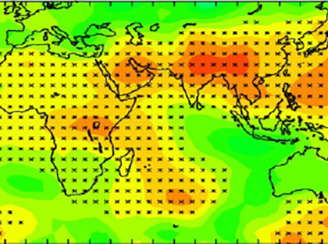 Trends in Global Tropospheric Ozone Inferred from a Composite Record of TOMS/OMI/MLS/OMPS Satellite Measurements and the MERRA-2 GMI Simulation
Trends in Global Tropospheric Ozone Inferred from a Composite Record of TOMS/OMI/MLS/OMPS Satellite Measurements and the MERRA-2 GMI SimulationOMI satellite measurements identify increases in tropospheric ozone over Saudi Arabia/India/Southeast Asia and other global regions
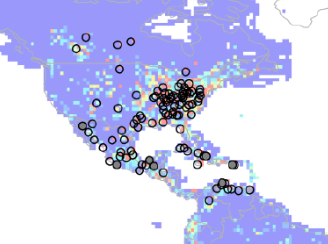 A new global anthropogenic SO2 emission inventory for the last decade
A new global anthropogenic SO2 emission inventory for the last decade A mosaic of satellite-derived and bottom-up emissions
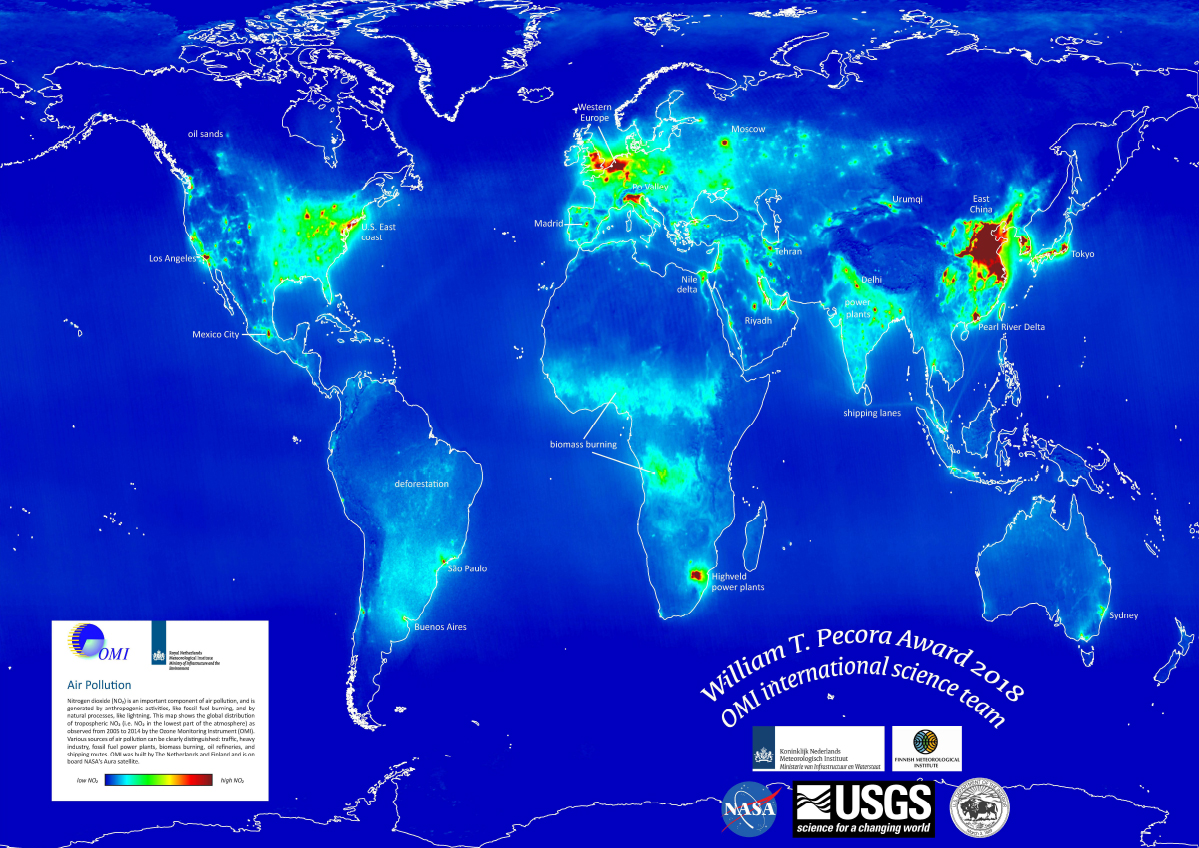 Aura OMI International Team Awarded USGS 2018 Pecora Award
Aura OMI International Team Awarded USGS 2018 Pecora Award The Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) International Team, consisting of Dutch, Finnish and American scientists, was awarded the 2018 William T. Pecora Award by the USGS.
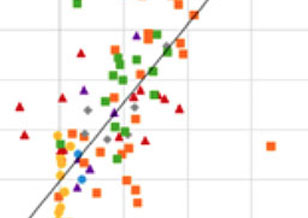 Nitrogen Dioxide Data to Show A Relationship Between Air Quality Changes & Economic Growth Globally
Nitrogen Dioxide Data to Show A Relationship Between Air Quality Changes & Economic Growth Globally Satellites offer an unprecedented opportunity to evaluate patterns and trends in air pollution, especially in regions with few or no ground-based monitors.
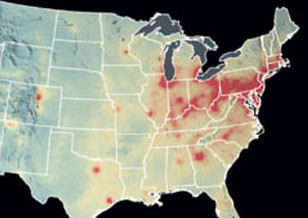 The 2018 National Academies’ Decadal Survey Highlights Aura Data to Demonstrate the Power of Satellite Data for Science & Societal Benefit
The 2018 National Academies’ Decadal Survey Highlights Aura Data to Demonstrate the Power of Satellite Data for Science & Societal Benefit In "Thriving on Our Changing Planet: A Decadal Strategy for Earth Observation from Space”, Aura data were presented as examples of satellite observations used as a global monitoring system for air quality & health and stratospheric ozone.