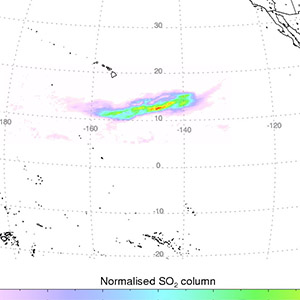
(movie) On May 20, 2006 a major lava dome collapse at the Soufriere Hills volcano triggered an explosive emission of volcanic gases. Sulfur dioxide in the resulting gas cloud was tracked by OMI for 3 weeks as it moved westwards across the Pacific.
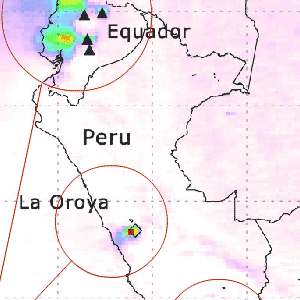
The Peruvian copper smelters are among the world's largest industrial point sources of sulfur dioxide (SO2), and are among the most polluting in the world. OMI is sensitive enough to identify copper being emitted from the La Oroya and Ilo smelters even though these produce less SO2 than the volcanoes.
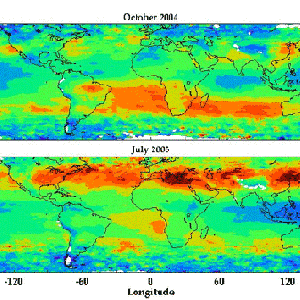
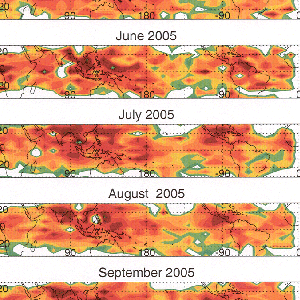
OMI & MLS can estimate the tropospheric ozone residual by subtracting the MLS stratospheric ozone from OMI column ozone. These maps show pollution streaming from the U.S., Europe and China to the west in summer and pollution from biomass burning in the equatorial zone.
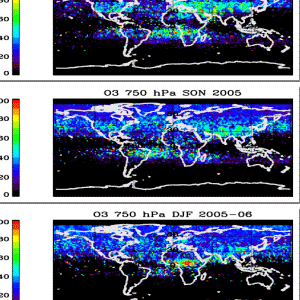
Coincident measurements of tropospheric ozone and carbon monoxide are critical for understanding chemical and dynamical processes, which can be very complex in the troposphere.
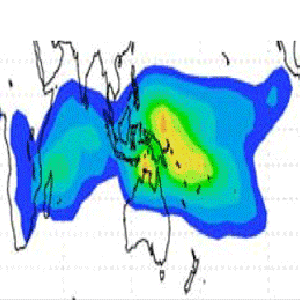
Cloud ice measurement will improve global circulation models used for weather and climate forecasts.
The measurements will also help quantify the upper tropospheric hydrological cycle, including water vapor feedbacks on climate change.
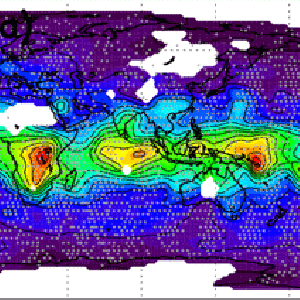
MLS sees cloud ice, but HIRDLS sees the clouds themselves, even clouds that are so thin that people cannot see them. Just as in the MLS cloud ice map we see large amounts of this cirrus in regions of significant cloud ice.
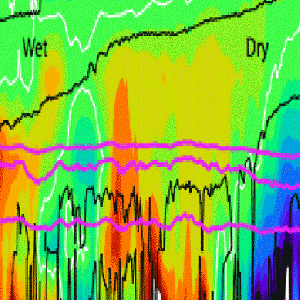
The hydrological cycle acts differently in different location. The TES measurements show that in the tropics, re-evaporation of precipitation is an important process controlling cloud formation. Up to 70% of precipitation is re-evaporated into the cloud.
CO is a signature of pollution and can be transported a long way from its source. Not surprisingly, that transport can be vertical as well as horizontal. These images show how CO detected in the lower stratosphere can tell us something about where convection is occurring.
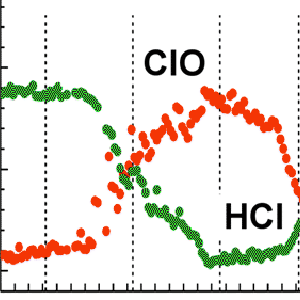
The continuous measurement of HCl in the stratosphere shows the rapid recovery of this major chlorine reservoir after polar ozone loss, and continues the long-term measurements from UARS HALOE. Monitoring HCl tells us about ozone loss processes and the recovery of the ozone layer.
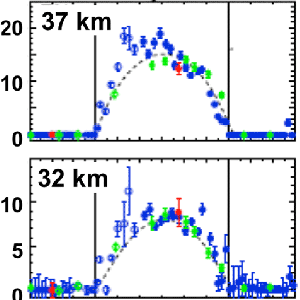
The MLS measurements of OH and HO2 have provided the first tests of global stratospheric hydrogen chemistry and resolved the disagreement between model estimates of OH and earlier observations - these data suggest earlier observations are suspect.
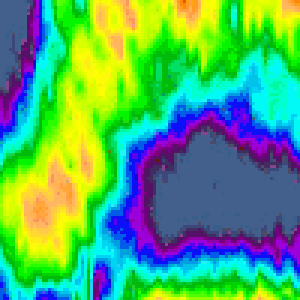
HIRDLS high resolution temperature measurements show short vertical wavelength gravity waves, permitting assessment of gravity wave forcing in the stratospheric circulation.
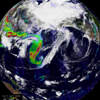
(movie)Asia is suffering through the worst dust storm season in at least five years. The eighth major storm this year clogged the air over China, Korea, and Japan with sand from the Taklamkan and Gobi deserts. The sand picks up a toxic mix of heavy metals and carcinogens as the clouds pass over China's industrial areas, exacerbating health problems due to these storms.
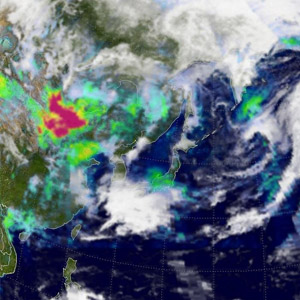
South Koreans were treated to a rare weather phenomenon on Monday when yellow snow fell in the capital and elsewhere across the country.
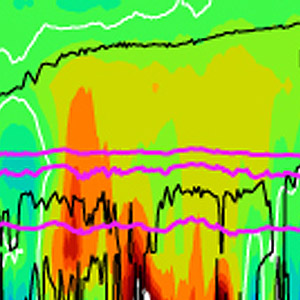
As tropical air rises into the stratosphere it carries with it trace gases, such as CFC's that are responsible for ozone depletion.